
The barrier potential for a silicon transistor is 0.7V at 25☌ and 0.3V at 25☌ for a germanium transistor. The proportional constant is the Gain (β).Īs discussed above, the transistor is a current controlled device which has two depletion layers with specific barrier potential required to diffuse the depletion layer. When a current flows through the diode D2, the diode D1 senses the current and a proportional current will be allowed to flow in the reverse direction from collector terminal to emitter terminal provided a higher potential is applied at the collector terminal. The diode D1 has a reverse conducting property based on the forward conduction of diode D2. An unbiased transistor or a transistor without potential applied at the terminals is similar to two diodes connected back-to-back as shown in figure below. As the power rating of the transistor increases necessary heat sink need to be attached to the body of transistor.

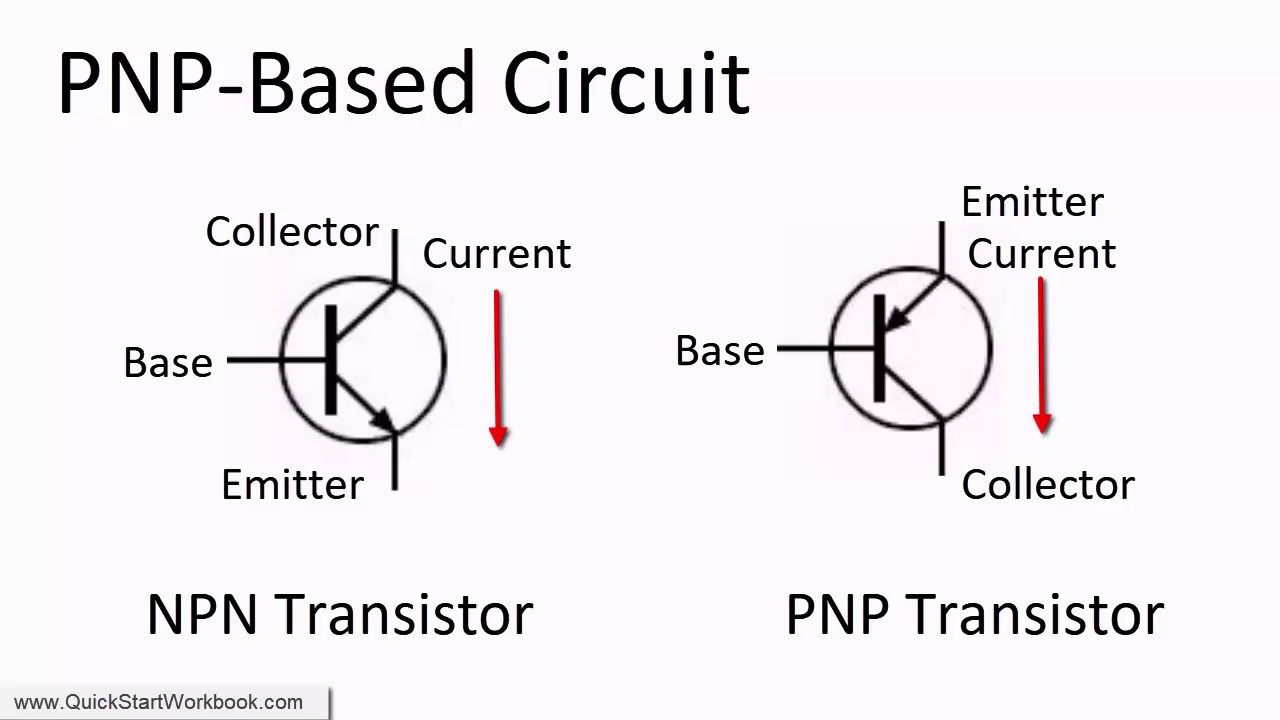
Let us consider the two examples of NPN transistors - BC547A and PN2222A, shown in the images above.īased on the fabrication process the pin configuration will change and the details will be available in corresponding datasheet. In this tutorial we will talk about the NPN transistors. There are two types of BJT - NPN and PNP transistors. Identifying the terminals of a transistor requires the pin diagram of a particular BJT part, it will be available in the datasheet. BJT is a three terminal device with Collector (C), Base (B) and Emitter (E). “Two polarities” is abbreviated as bipolar, hence the name Bipolar junction transistor. The first bipolar junction transistor was invented in 1947 at Bell laboratories.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
